 BACKGROUND
BACKGROUNDThe Saint-Etienne Proof House was created by royal appointment in 1782. In 1960, testing became compulsory for all civilian firearms and in 2010, the institution was called “Banc National d’Epreuve“.

With user safety in mind, the testing is focused on checking the resistance of the firearm. Following examination by a sworn test officer who checks the condition of the barrel, the inner dimensions, the locking and percussion mechanisms, the firearm is tested by firing over-pressure cartridges. A second in-depth examination is carried out after firing. Approved small arms are then marked, certified and registered.
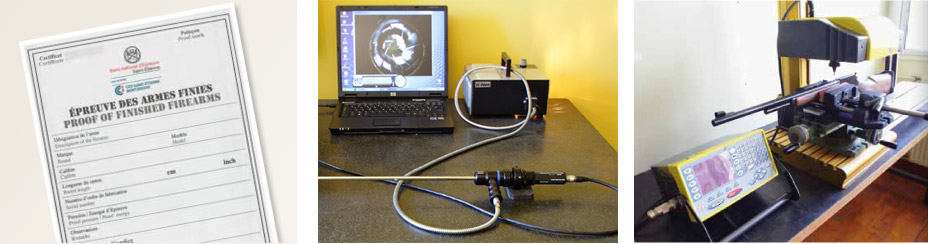

From 1914, the French proof house and four other European proof houses shared their procedures and 1969 saw the arrival of an international convention laying down international firearms testing standards. The signatory countries agree on the mutual acceptance of the proof marks of each country, in their territory. The member states incorporate the standards produced by the C.I.P. into their national legislation.
For further details: www.cip-bobp.org